Preparing for a SQL Server interview can be both exciting and challenging. Whether you’re a fresh graduate looking to break into database administration or an experienced professional aiming to advance your career, mastering SQL Server interview questions is crucial for success. This comprehensive guide covers everything from fundamental concepts to advanced techniques, providing you with the knowledge and confidence needed to excel in your next SQL Server interview

Professional SQL Server interview preparation guide cover design with database elements
Understanding SQL Server Interview Landscape
SQL Server interviews typically assess candidates across multiple dimensions, from basic database concepts to complex performance optimization scenarios. The interview process usually involves a combination of theoretical questions, practical coding challenges, and scenario-based problem-solving exercises
Modern SQL Server interviews have evolved to focus heavily on real-world application scenarios rather than just memorization of syntax. Employers are increasingly looking for candidates who can demonstrate not only technical knowledge but also the ability to solve business problems using SQL Server technologies
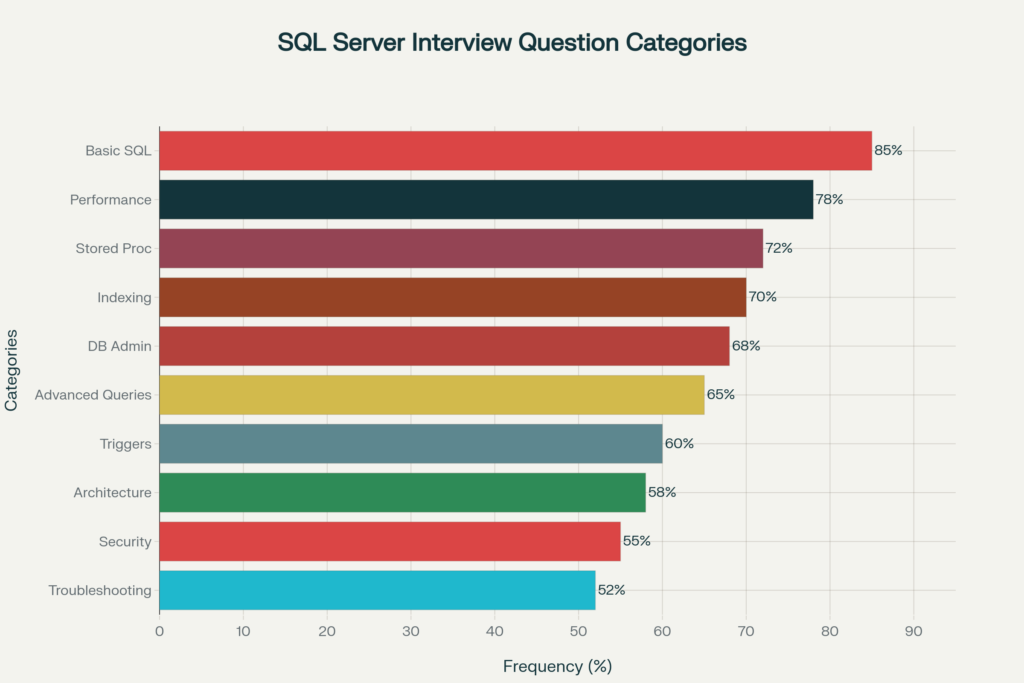
Most Common SQL Server Interview Question Categories – Frequency and Importance Analysis
Beginner Level Questions and Answers
Core SQL Server Concepts
What is SQL Server and what are its key features?
SQL Server is Microsoft’s relational database management system (RDBMS) designed for enterprise-level applications. It manages data efficiently from storage to retrieval and supports a wide range of data types, ensuring high availability, security, and performance
Key features include:
- ACID Properties: Ensures data integrity through Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability
- T-SQL Support: Extended version of SQL with additional programming constructs
- Scalability: Handles large datasets and concurrent users effectively
- Security: Robust authentication and authorization mechanisms
- High Availability: Features like Always On Availability Groups and failover clustering
What are the different data types in SQL Server?
SQL Server supports various data types categorized into several groups
- Numeric Types: INT, BIGINT, DECIMAL, FLOAT, REAL
- Character Types: VARCHAR, NVARCHAR, CHAR, NCHAR, TEXT
- Date/Time Types: DATETIME, DATE, TIME, DATETIME2, DATETIMEOFFSET
- Binary Types: BINARY, VARBINARY, IMAGE
- Other Types: BIT, UNIQUEIDENTIFIER, XML, JSON (in newer versions)
Understanding data type selection is crucial for optimal storage and performance
JOIN Operations
What are the different types of JOINs in SQL Server?
SQL Server supports several JOIN types for combining data from multiple tables
- INNER JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables
- LEFT JOIN (LEFT OUTER JOIN): Returns all records from the left table and matched records from the right table
- RIGHT JOIN (RIGHT OUTER JOIN): Returns all records from the right table and matched records from the left table
- FULL OUTER JOIN: Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right table
- CROSS JOIN: Returns the Cartesian product of both tables
Here’s a practical example:
sql-- INNER JOIN Example
SELECT e.EmployeeName, d.DepartmentName
FROM Employees e
INNER JOIN Departments d ON e.DepartmentID = d.DepartmentID;
-- LEFT JOIN Example
SELECT c.CustomerName, o.OrderDate
FROM Customers c
LEFT JOIN Orders o ON c.CustomerID = o.CustomerID;
Intermediate Level Questions and Answers
Performance Tuning Fundamentals
How do you identify slow-running queries in SQL Server?
Identifying slow-running queries is essential for database performance optimization. Several techniques can help:
Query Store Analysis: SQL Server’s Query Store captures query performance metrics over time, allowing you to identify consistently slow queries.
Dynamic Management Views (DMVs): Use DMVs like sys.dm_exec_query_stats to find resource-intensive queries:
sqlSELECT TOP 10
qs.total_elapsed_time / qs.execution_count AS avg_elapsed_time,
qs.total_logical_reads / qs.execution_count AS avg_logical_reads,
qt.text AS query_text
FROM sys.dm_exec_query_stats qs
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(qs.sql_handle) qt
ORDER BY avg_elapsed_time DESC;
SQL Server Profiler and Extended Events: These tools capture real-time query execution data, helping identify performance bottlenecks910.
Stored Procedures and Functions
What is a stored procedure and how do you create one?
A stored procedure is a prepared SQL code collection that can be saved and reused multiple times. It’s a powerful feature that encapsulates business logic within the database.
Benefits of Stored Procedures:
- Performance: Precompiled execution plans improve performance
- Security: Reduces SQL injection risks
- Reusability: Can be called from multiple applications
- Maintainability: Centralized business logic
Creating a Basic Stored Procedure:
sqlCREATE PROCEDURE GetEmployeesByDepartment
@DepartmentID INT
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT
EmployeeID,
EmployeeName,
Position,
Salary
FROM Employees
WHERE DepartmentID = @DepartmentID
ORDER BY EmployeeName;
END;
-- Execute the stored procedure
EXEC GetEmployeesByDepartment @DepartmentID = 5;
Indexing Strategies
What’s the difference between clustered and non-clustered indexes?
Understanding indexing is crucial for SQL Server performance optimization.
Clustered Index:
- Determines the physical order of data rows in a table
- Each table can have only one clustered index
- The table data is stored in the order of the clustered index key
- Automatically created when you define a PRIMARY KEY constraint
Non-Clustered Index:
- Creates a separate structure that points to data rows
- A table can have multiple non-clustered indexes (up to 999)
- Contains pointers to the actual data rows
- Takes additional storage space
sql-- Creating a clustered index
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX IX_Employee_ID
ON Employees (EmployeeID);
-- Creating a non-clustered index
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX IX_Employee_LastName
ON Employees (LastName);
Index Design Guidelines:
- Use clustered indexes on unique, sequential columns
- Create non-clustered indexes on frequently searched columns
- Avoid over-indexing as it impacts INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE performance
- Consider covering indexes for frequently used queries
Advanced Level Questions and Answers
Query Optimization Techniques
How do you optimize a poorly performing query?
Query optimization is a systematic process that involves multiple techniques:
1. Execution Plan Analysis:
Start by examining the query execution plan to identify bottlenecks:
sql-- Enable actual execution plan
SET STATISTICS IO ON;
SET STATISTICS TIME ON;
SELECT * FROM Orders o
INNER JOIN Customers c ON o.CustomerID = c.CustomerID
WHERE o.OrderDate >= '2023-01-01';
2. Index Optimization:
- Add missing indexes identified in the execution plan
- Remove unused indexes that impact write performance
- Consider composite indexes for multi-column WHERE clauses
3. Query Rewriting Techniques:
- Replace correlated subqueries with JOINs when possible
- Use EXISTS instead of IN for better performance
- Avoid SELECT * and specify only required columns
4. Statistics Updates:
Ensure table statistics are current for optimal query plans:
sql-- Update statistics for better query optimization
UPDATE STATISTICS TableName;
High Availability Solutions
What are Always On Availability Groups?
Always On Availability Groups provide high availability and disaster recovery solutions for SQL Server. Key features include:
- Multiple Readable Secondary Replicas: Distribute read workloads
- Automatic Failover: Minimize downtime during failures
- Backup Offloading: Perform backups on secondary replicas
- Cross-Platform Support: Works with Linux and container environments
Configuration Example:
sql-- Create availability group
CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP MyAG
WITH (AUTOMATED_BACKUP_PREFERENCE = SECONDARY)
FOR DATABASE MyDatabase
REPLICA ON
'Server1' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = 'TCP://Server1:5022',
AVAILABILITY_MODE = SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
FAILOVER_MODE = AUTOMATIC),
'Server2' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = 'TCP://Server2:5022',
AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL);
Database Administration
How do you troubleshoot deadlock situations?
Steps and methods for diagnosing deadlock situations in SQL Server, useful for DBA interview preparation
1. Deadlock Detection and Analysis:
- Enable deadlock monitoring using Extended Events
- Analyze deadlock graphs to understand lock contention
- Review system and application logs for patterns
sql-- Create Extended Event session for deadlock monitoring
CREATE EVENT SESSION DeadlockMonitor ON SERVER
ADD EVENT sqlserver.xml_deadlock_report
ADD TARGET package0.event_file(SET filename='C:\DeadlockTrace.xel');
ALTER EVENT SESSION DeadlockMonitor ON SERVER STATE = START;
2. Prevention Strategies:
- Ensure consistent lock order across transactions
- Use appropriate isolation levels
- Keep transactions short and focused
- Implement proper indexing to reduce lock duration
Advanced Triggers and Automation
What are triggers and when would you use them?
Triggers are special stored procedures that automatically execute in response to specific database events.
Types of Triggers:
DML Triggers: Fire on INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations
sqlCREATE TRIGGER trg_AuditEmployee
ON Employees
AFTER UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
INSERT INTO EmployeeAudit (
EmployeeID,
OldSalary,
NewSalary,
ModifiedBy,
ModifiedDate
)
SELECT
d.EmployeeID,
d.Salary,
i.Salary,
SYSTEM_USER,
GETDATE()
FROM deleted d
INNER JOIN inserted i ON d.EmployeeID = i.EmployeeID
WHERE d.Salary <> i.Salary;
END;
DDL Triggers: Fire on schema changes like CREATE, ALTER, DROP
Logon Triggers: Fire when users establish sessions
Use Cases for Triggers:
- Audit trail implementation
- Business rule enforcement
- Data validation beyond constraints
- Automatic data synchronization
- Security monitoring
Scenario-Based Interview Questions
Real-World Problem Solving
Database Migration Scenario:
“You need to migrate a 500GB production database to a new server with minimal downtime. How would you approach this?”
Comprehensive Migration Strategy:
- Assessment Phase:
- Analyze current database size, growth patterns, and usage
- Identify peak and off-peak hours
- Document dependencies and linked servers
- Preparation Phase:
- Set up target environment with identical configuration
- Perform full backup and test restore procedures
- Plan rollback strategies
- Execution Phase:
- Use backup/restore with tail-log backup for minimal downtime
- Consider Always On Availability Groups for zero-downtime migration
- Implement database mirroring for seamless failover
- Validation Phase:
- Verify data integrity using CHECKDB
- Test application connectivity and performance
- Monitor system resources and performance metrics
Performance Troubleshooting Scenario
Query Performance Issue:
“A critical report query that used to run in 30 seconds now takes 10 minutes. How do you diagnose and fix this?”
Systematic Troubleshooting Approach:
- Immediate Assessment:
- Check for blocking sessions using
sp_who2 - Review recent schema changes or index modifications
- Analyze current system resource utilization
- Check for blocking sessions using
- Historical Analysis:
- Compare current execution plans with historical baselines
- Check Query Store for performance regression patterns
- Review recent data volume changes
- Root Cause Analysis:
- Update table statistics:
UPDATE STATISTICS TableName WITH FULLSCAN - Identify missing indexes from execution plan recommendations
- Check for parameter sniffing issues
- Update table statistics:
- Resolution Implementation:
- Implement recommended indexes
- Consider query rewriting for better performance
- Update statistics maintenance schedules
Best Practices for Interview Success
Technical Preparation Strategies
Hands-On Practice:
- Set up a local SQL Server instance for practice
- Work through real-world scenarios and case studies
- Practice explaining complex concepts in simple terms
- Build a portfolio of solved problems and optimizations
Knowledge Areas to Master:
- Core SQL Skills: Advanced querying, joins, subqueries, CTEs
- Performance Tuning: Index design, query optimization, execution plans
- Database Design: Normalization, schema design, best practices
- Administration: Backup/recovery, security, monitoring, maintenance
- Advanced Features: Always On, replication, partitioning, compression
Interview Communication Tips
Structured Problem Solving:
- Clarify Requirements: Ask questions to understand the full scope
- Explain Your Approach: Walk through your thought process step-by-step
- Consider Alternatives: Discuss multiple solutions and trade-offs
- Think Aloud: Verbalize your reasoning as you work through problems
- Validate Solutions: Explain how you would test and verify your approach
Behavioral Questions Preparation:
- Prepare examples of challenging technical problems you’ve solved
- Practice explaining technical concepts to non-technical audiences
- Develop stories that demonstrate leadership and collaboration skills
- Be ready to discuss continuous learning and professional development
Conclusion
Success in SQL Server interviews requires a combination of solid technical knowledge, practical experience, and strong communication skills. This comprehensive guide covers the essential topics from basic concepts to advanced optimization techniques, providing you with the foundation needed to excel in your interview.
Remember that interviews are not just about demonstrating what you know, but also about showing how you think, learn, and solve problems. Practice regularly, stay current with SQL Server developments, and approach each interview as an opportunity to showcase your passion for database technology and your commitment to continuous improvement.
The key to interview success lies in thorough preparation, hands-on practice, and the confidence that comes from truly understanding SQL Server technologies. Use this guide as your roadmap, but don’t forget to supplement it with practical experience and ongoing learning. Good luck with your SQL Server interview journey!







Leave a Reply